See the Best Option for Retinal Detachment Surgery!
What Is Retinal Detachment Surgery?
Retinal detachment surgery is a medical procedure performed to repair a detached or torn retina, which is a serious eye condition that can lead to permanent vision loss if not treated promptly. The surgery aims to reattach the retina to its normal position on the back of the eye, allowing it to function correctly.
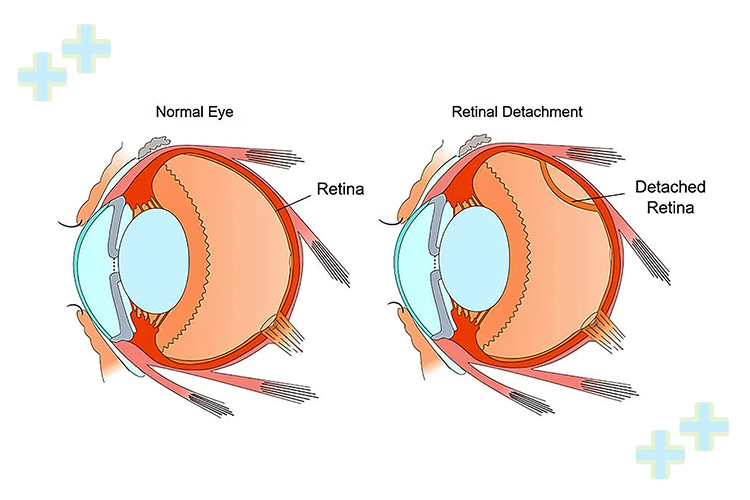
What Are the Symptoms of Retinal Detachment?
Symptoms of retinal detachment may include:
- Sudden appearance of floaters (small, dark spots or specks that float across your field of vision)
- Light flashes in 1 of the eyes or in both the eyes
- Blurred vision
- Reduced peripheral vision.
- A shadow or curtain-like effect in your field of vision
- Sudden and severe vision loss
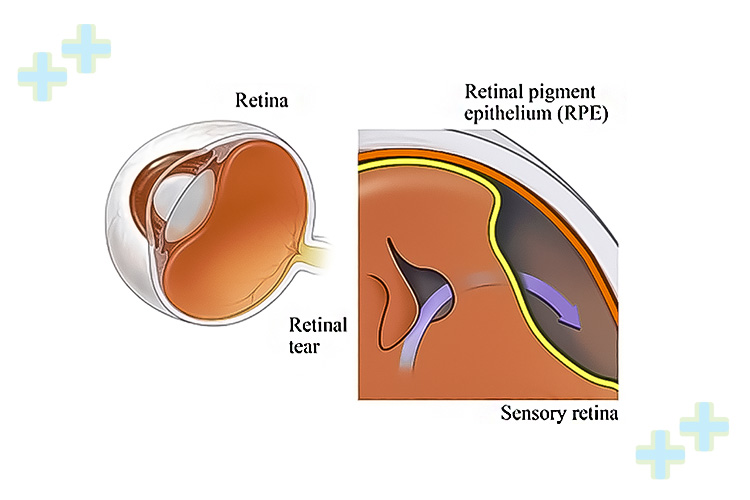
How to Diagnose Retinal Detachment?
To diagnose retinal detachment, your eye doctor will perform a thorough eye examination, including dilating your pupils to examine the retina more closely. Other tests may be needed, such as ultrasound imaging, to help confirm the diagnosis.
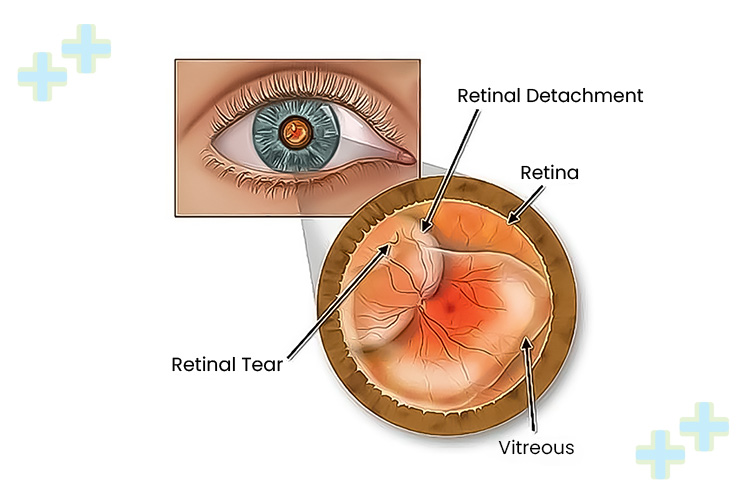
How to Treat Retinal Detachment with Retinal Detachment Surgery?
Treating retinal detachment typically involves doing a surgery for reattaching the patient’s retina back of his eye. There are several surgical options for this, which include the following:
- Scleral buckle surgery: A silicone or plastic band is placed around the eye to push the wall of the eye closer to the detached retina, allowing it to reattach.
- Vitrectomy: The vitreous gel is removed from the eye and replaced with a gas or silicone oil bubble, which helps to push the retina back into place.
- Pneumatic retinopexy: A gas bubble is injected into the eye, which pushes the detached retina back into place.
Health Trawell Can Be Your Travel Partner for Retinal Detachment Surgery in India!
After the Retinal Detachment Surgery, patients will need to follow specific instructions for care and recovery, including avoiding strenuous activity, keeping their head in a certain position, and using eye drops as prescribed. Regular follow-up appointments with their eye doctor are also essential to monitor healing and ensure proper vision restoration. All this while when you are in India on your medical tour for the surgery, Health Trawell is going to escort your guide you all through!
Transplanted stem cells after infusion through the central line, travels through the blood and enters the bone marrow, where they get deposited. In some time they multiply and produce new blood cells. This process of graft uptake and multiplication is called engraftment. Normally it takes several weeks before the bone marrow is able to produce blood cells to the normal level.
During the follow-up period regular check-ups and blood tests may be needed to monitor a patient’s condition and progress. Close medical supervision is required for a few days after the BMT. In case of any signs of complication or infection, the patient may need to be treated with hospitalisation.
After bone marrow transplant, the recipient must remain under close medical care for a few weeks. If there are any signs of infection or other complications, the recipient may need to stay in the hospital for several days or sometimes longer. Patients have to stay near the hospital for a few weeks or months after the transplant, to allow for close monitoring. Length of stay usually depends on the type of transplant and possibility of complications.
Time to time blood or its component transfusions may be needed in the post- transplant period till patients’ own bone marrow starts producing enough cells.
A BMT patient remains at a higher risk of infections for months or years after the transplant. Regular life-long follow-up is done to look for any signs of infection at the earliest.
OUR SERVICES

Cosmetic Surgery

Spine Surgery

Organ Transplant

Orthopedic Surgery

Gynecology Infertility

Ophthalmology

Neurosurgery
Cardiology
YOUR GATEWAY TO HEALTH

